
- Setting up an OOT
- Path to scaling agile
Why do we need Omnichannel?
Customer experience expectations are changing faster than ever before. Customers expect every business they engage with to deliver great customer experiences. It is crucial for BD to strengthen Omnichannel capabilities to deliver truly inspiring customer experiences and to differentiate BD in a highly competitive environment.
What is needed to enable Omnichannel?
To enable true Omnichannel, teams need to operate with speed, be responsive and relevant in each customer interaction over the lifetime of the customer journey. One way to deliver that is through a strong team that adheres to agile principles of working. We call that an omnichannel orchestration team, or OOT for short.
An OOT is a cross-functional, agile team responsible for defining the marketing strategy and executing test-and-learn campaigns.
OOT’s leverage proven agile strategies like Scrum to guide new management practices and ways of working to respond to rapidly changing customer needs.
-

Time-saving and repeatable processes
Repeatable processes that are quick to implement and scale
-
Internal data-driven results
Emergence of data-driven campaigns that refine the understanding of the customer via “test and learn”
-

Empowered decision-making to react to data
Efficiency-driven processes and ceremonies driven by a connected team with internal capability built for campaigns
-

Reducing risk through customer-centricity and iteration
Iterative campaign roll out reduces downside risk
-

Customer-centric, persona-driven, qualified leads
Higher volume and better converting leads driven by personas shared across BUs
The approach to setting up and scaling OOTs begins by establishing an OOT for one BU and one BD product, and then scaling across the BU
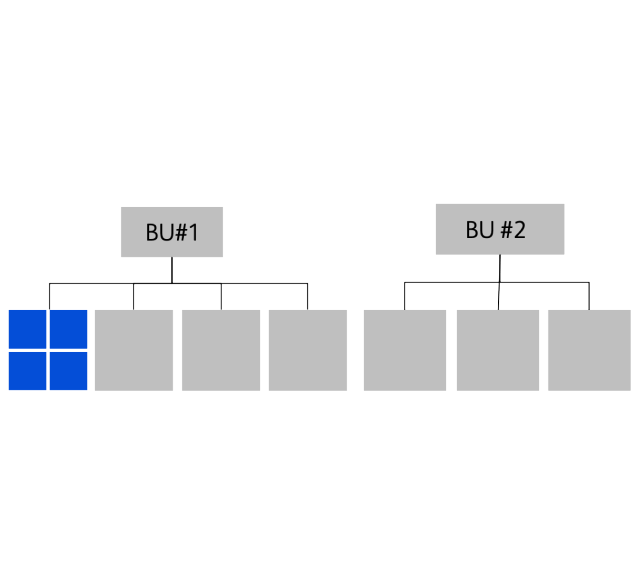
- OOT team delivers “test and learn” campaigns to decrease campaign risk
- Iterative campaigns drive deeper customer understanding and more prudent spending
- New ways of working are learned and tested within individual use cases
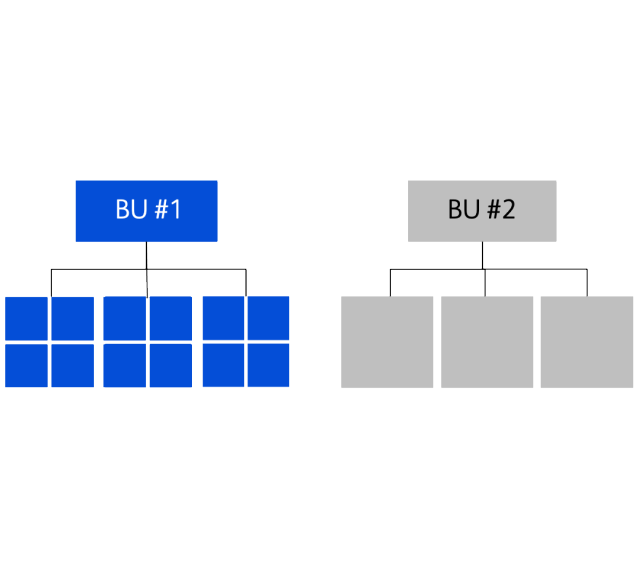
- Further synergies (communication, resource allocation) can be achieved by expanding model across BU
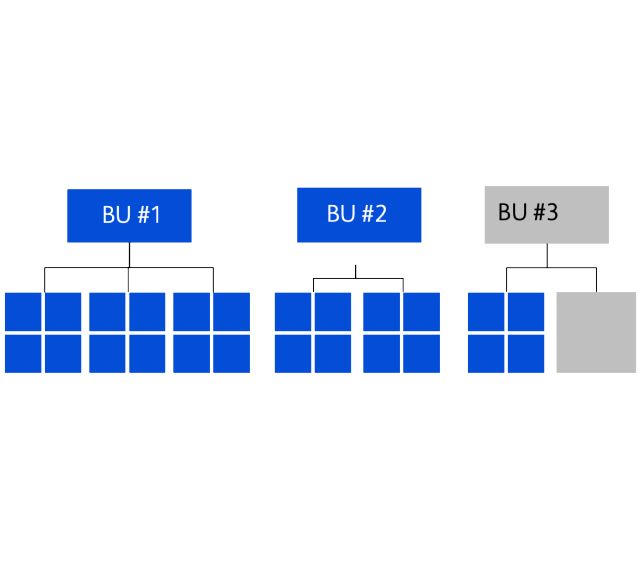
- Creation of common customer views across BU to help enable better coordination across teams, and true Omnichannel experiences
- Ability for cross-functional understanding to enable shared customer lists and cross-selling
- Ability to achieve 30% gains in marketing efficiency driven by increased cross-functional team coordination and output
- There is clear standardization of processes and roles allowing more interoperability
- Teams share a common customer definition and single source of truth data source
- True Omnichannel is delivered to the prospective customer